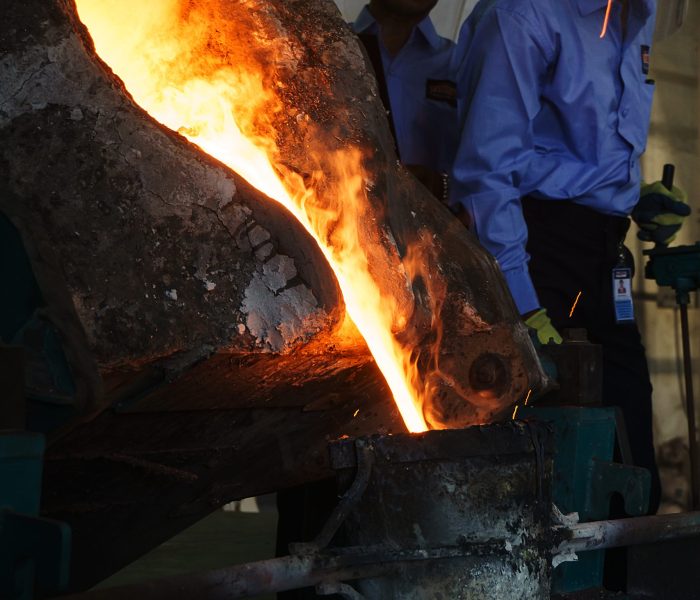
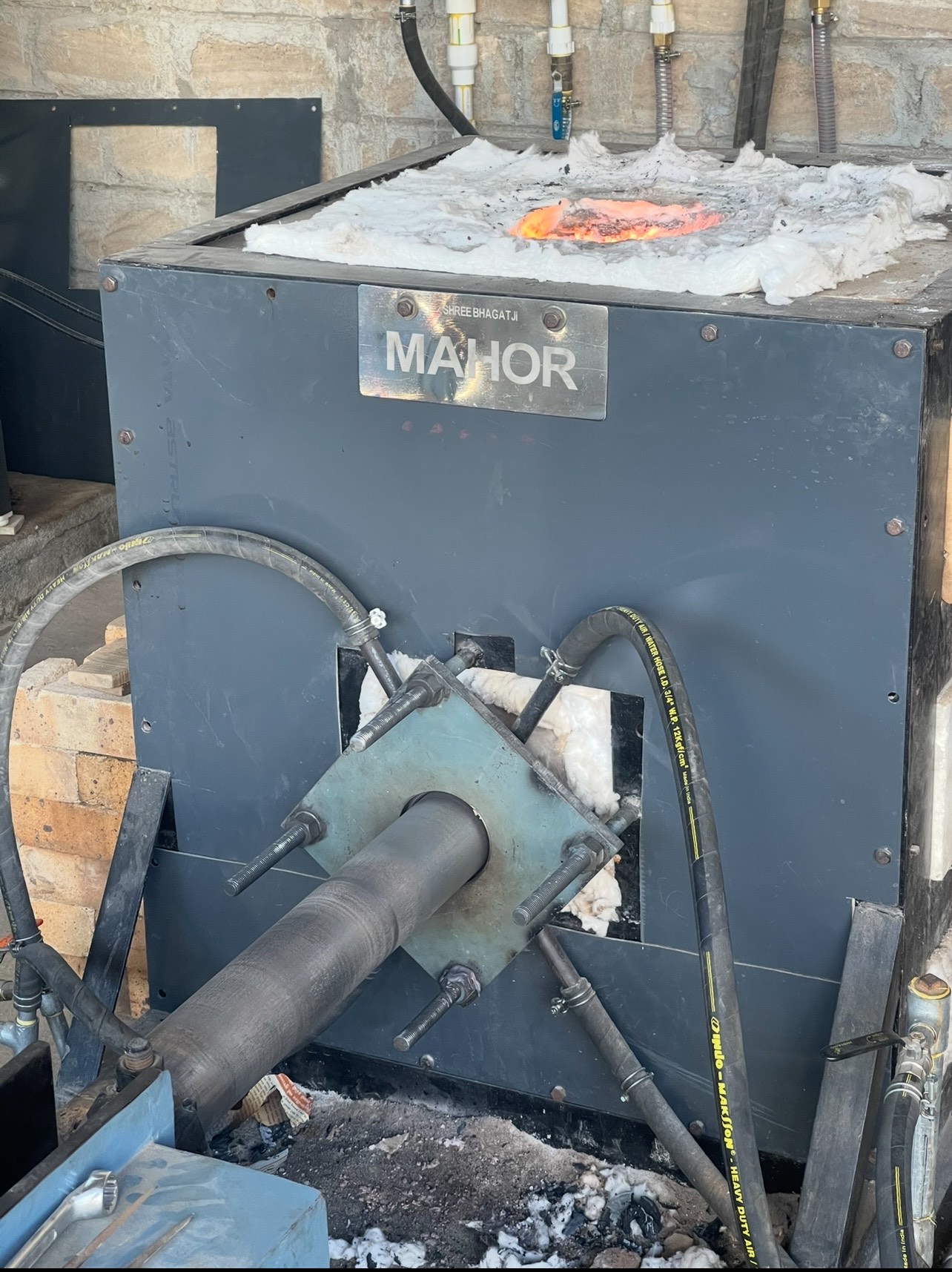
Material Melting
The bronze casting process involves several steps, with the melting of bronze being a critical phase. Here’s a detailed explanation of the bronze melting process:- Raw Materials: Bronze is an alloy primarily composed of copper and tin. Other elements like aluminum, nickel, or zinc may be added depending on the alloy type.
- Sorting: Raw materials are inspected and sorted to ensure quality.
- Cleaning: Impurities, dirt, and oils are removed to avoid contamination during melting.
Continuous casting
A Modern Approach Continuous casting is a revolutionary process in the metal industry, and bronze is no exception. This method offers several advantages over traditional casting techniques, making it a preferred choice for many manufacturers.
The Process In continuous casting, molten bronze is poured into a water-cooled mold. As the metal cools and solidifies, it is gradually withdrawn from the mold using rollers. This process continues uninterrupted, creating a continuous stream of bronze in the desired shape, such as rods, bars, or tubes.
Key Advantages
• Improved Quality: The controlled cooling process in continuous casting results in a more uniform microstructure and better mechanical properties, such as increased strength and ductility.
• Reduced Waste: By minimizing the formation of defects and optimizing material usage, continuous casting significantly reduces waste compared to traditional methods.
•Versatility: Continuous casting can be adapted to produce a wide range of bronze alloys and shapes, making it a versatile manufacturing process.
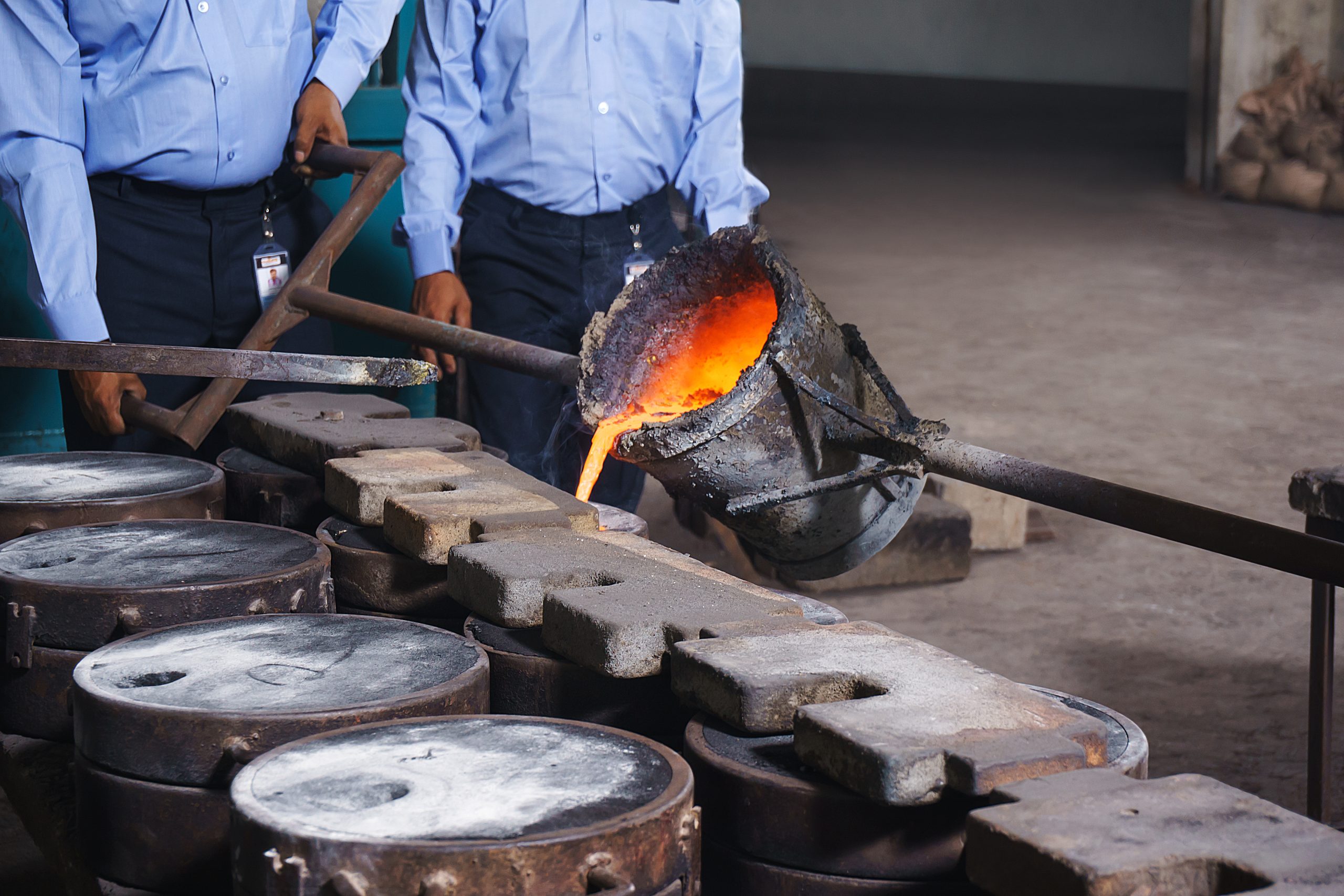


Material Pouring
A Crucial Step in Casting Pouring molten non-ferrous metals into molds is a critical stage in the casting process. It directly impacts the quality, integrity, and success of the final product.
Key Considerations for Pouring Non-Ferrous Metals:
Metal Temperature:
Proper Temperature: Each non-ferrous metal has a specific temperature range for optimal pouring. Pouring at too low a temperature can lead to incomplete filling of the mold, while pouring at too high a temperature can cause excessive oxidation, gas entrapment, and dimensional inaccuracies.
Temperature Control: Maintaining consistent temperature throughout the pouring process is crucial. This often involves using temperature sensors and controlling the heating source.
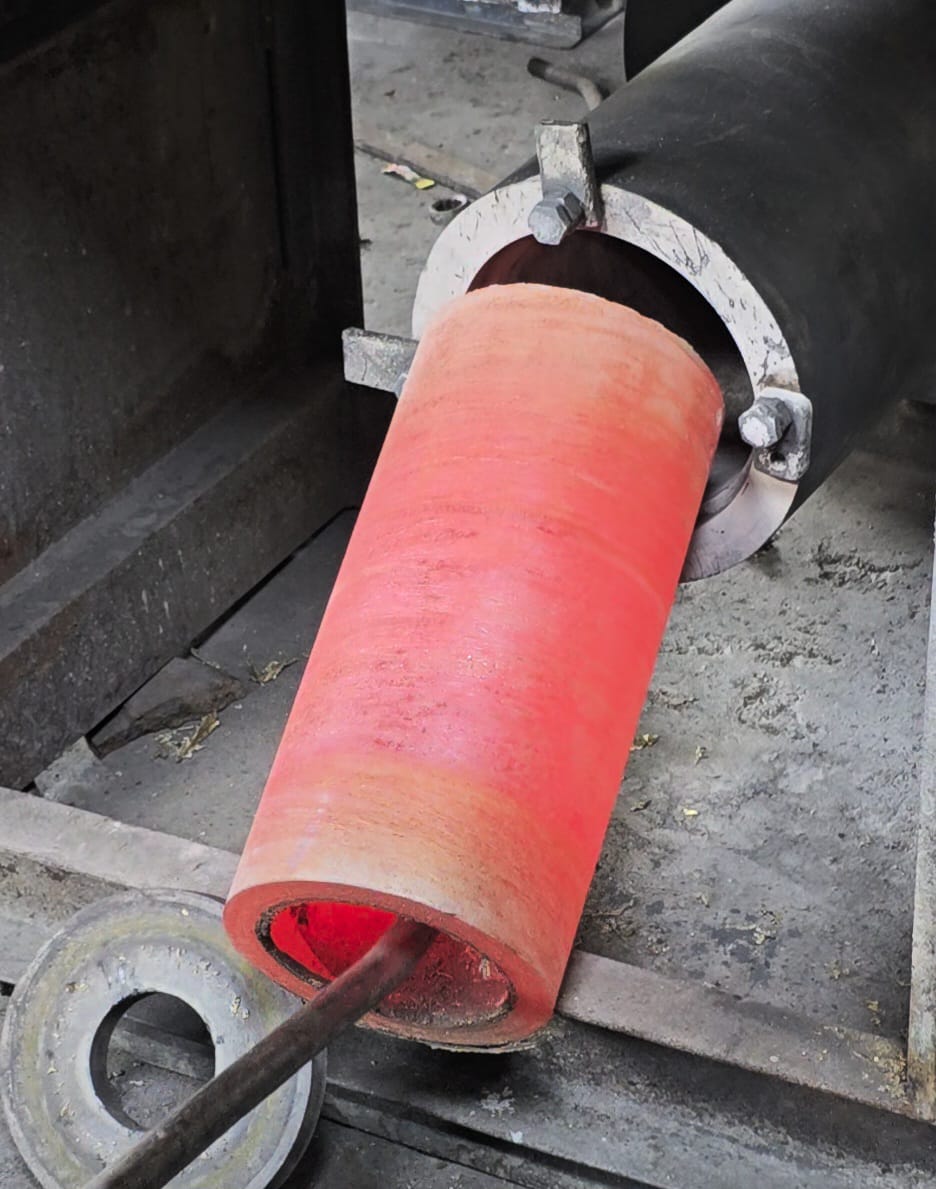
Centrifugal Casting
Non-Ferrous Centrifugal Casting: A Precision Casting Technique
Centrifugal casting is a specialized metal casting process where molten metal is poured into a mold that rotates at high speed. This centrifugal force distributes the metal evenly against the mold walls, resulting in dense, high-quality castings with superior mechanical properties.
The Process:
Mold Preparation: A mold, typically made of metal or ceramic, is prepared with a specific internal shape to create the desired casting.
Metal Melting: The chosen non-ferrous metal (such as aluminum, copper, or bronze alloys) is melted in a furnace to the appropriate temperature.
Pouring: The molten metal is poured into the rotating mold.
Solidification: As the mold spins, the centrifugal force pushes the molten metal against the mold walls, where it solidifies into the desired shape.
Cooling and Extraction: Once the casting has solidified, the mold is cooled, and the casting is extracted.
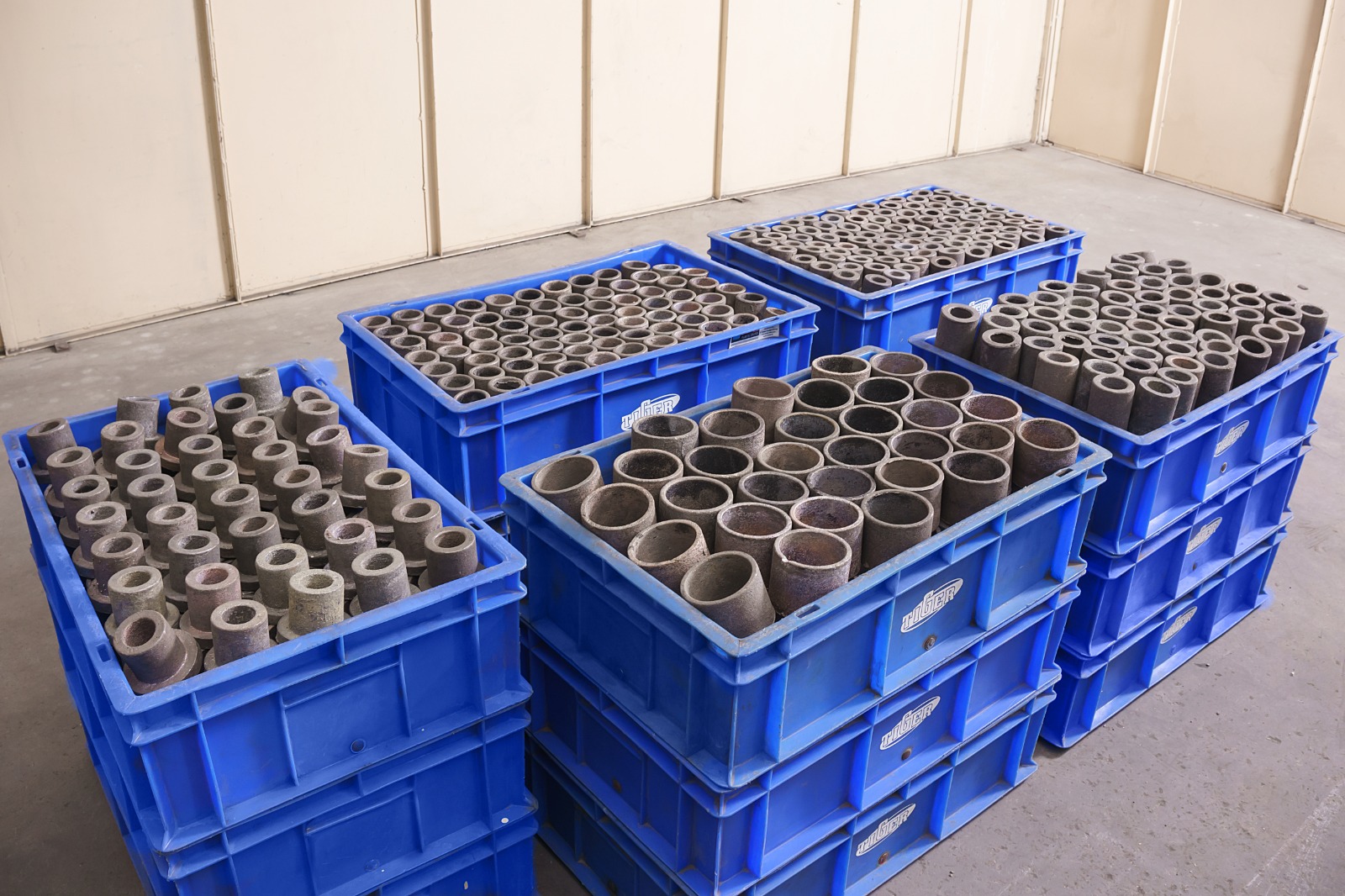


Sand cast Parts
A Timeless Technique Bronze sand casting is a traditional yet versatile method for creating intricate and durable bronze components. It involves creating a mold from sand and then pouring molten bronze into it to solidify. The Process: Pattern Making: A pattern, typically made of wood or metal, is created in the exact shape of the desired casting. Mold Preparation: The pattern is placed in a flask (a box-like container) and surrounded by sand. A binding agent is added to the sand to give it strength. Mold Cavity Creation: The pattern is carefully removed from the sand, leaving behind a hollow cavity in its shape. Pouring: Molten bronze is poured into the mold cavity through a sprue (a channel) in the sand. Solidification: The molten bronze cools and solidifies within the mold. Mold Removal: The sand mold is broken away to reveal the finished bronze casting.Aluminium pressure die cast parts
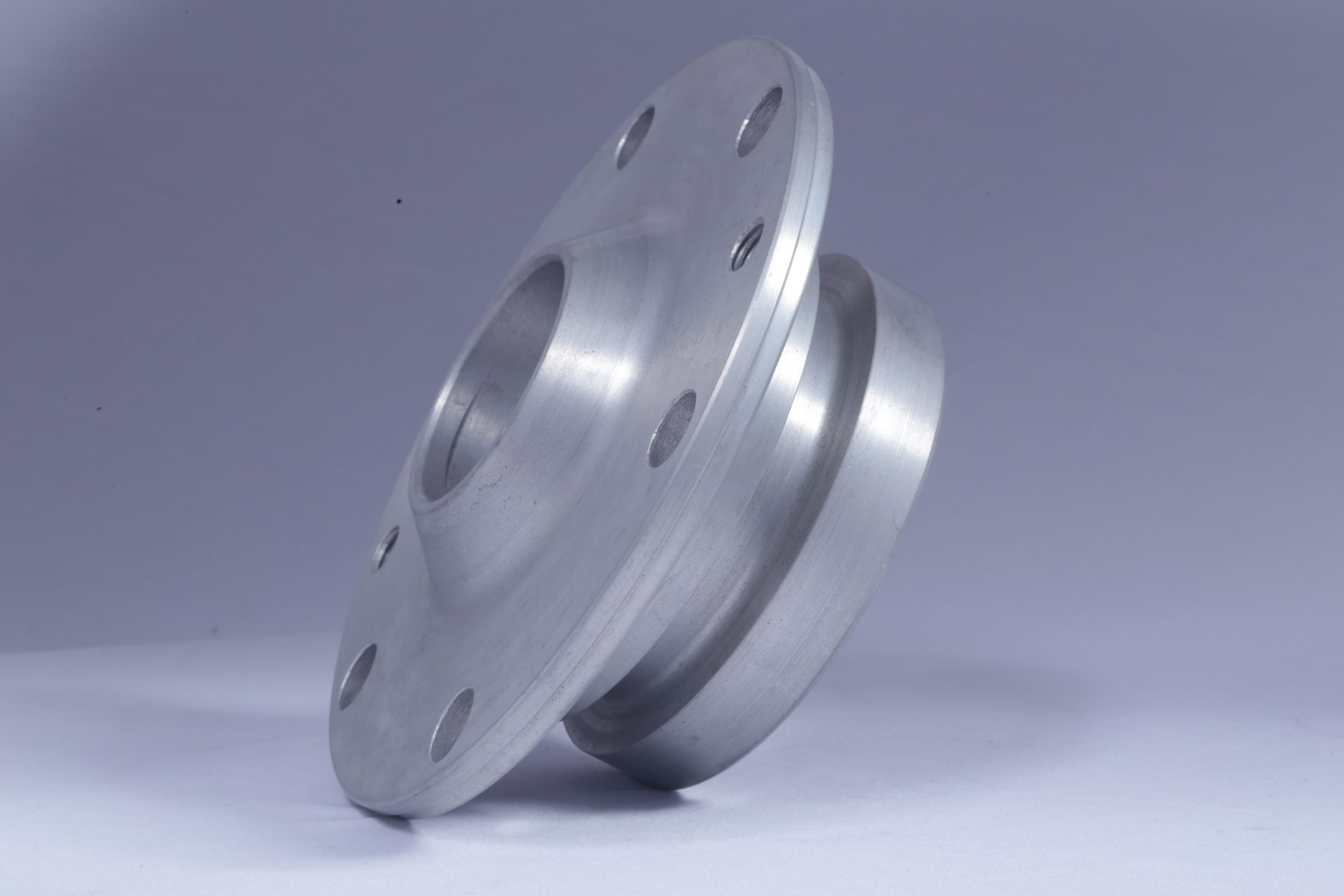
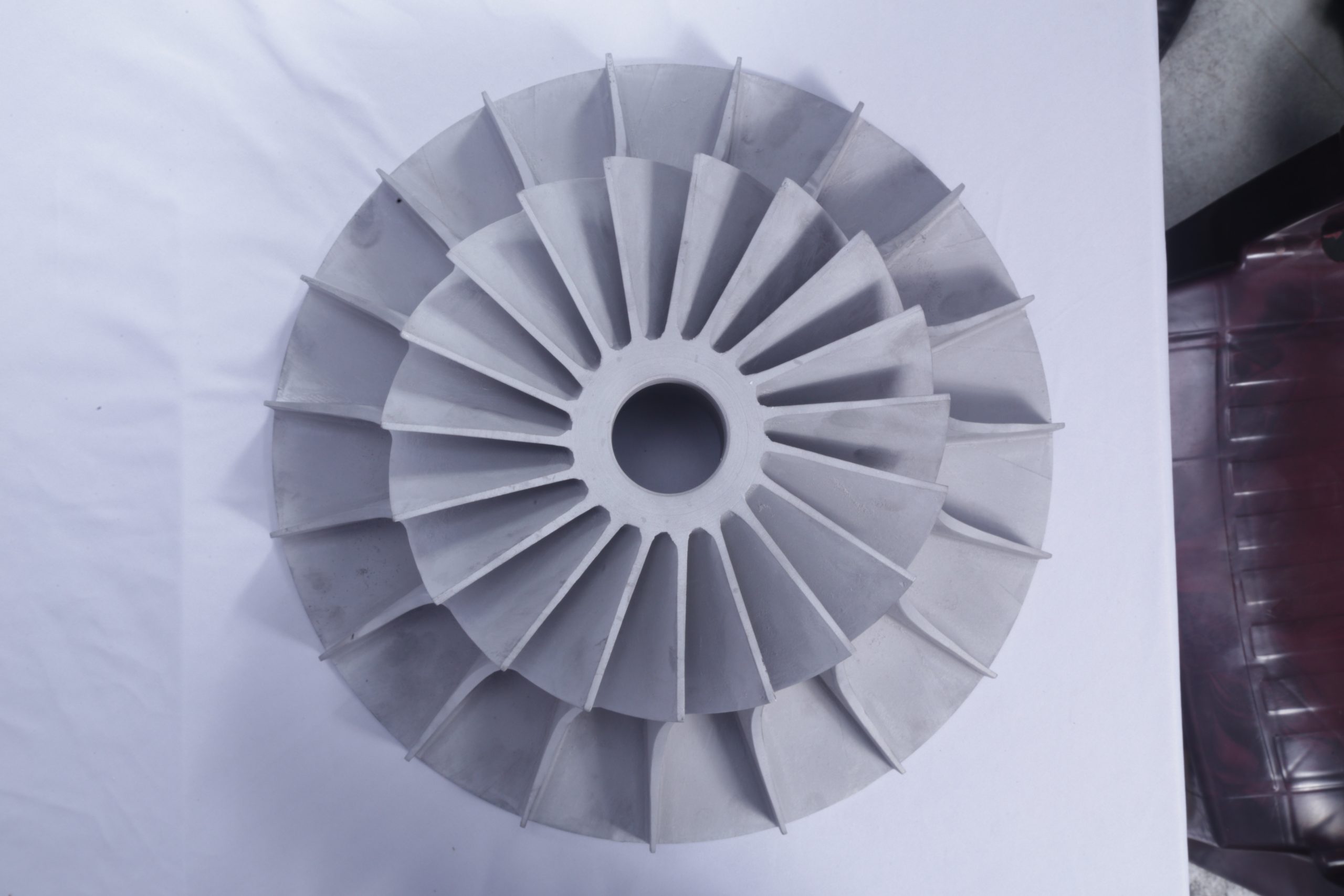
Aluminum Pressure Die Cast Parts: A Versatile Manufacturing Solution
Aluminum pressure die casting is a highly efficient and versatile manufacturing process used to create complex metal components with intricate details. It involves injecting molten aluminum under high pressure into a reusable metal mold (die). This process results in high-quality parts with excellent dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
Key Advantages of Aluminum Pressure Die Cast Parts:
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Aluminum is a lightweight metal with excellent strength, making it ideal for applications where weight reduction is crucial, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries.
Dimensional Accuracy and Consistency: The high-pressure injection process ensures precise dimensional control, minimizing the need for extensive machining.
Complex Shapes and Intricate Details: Pressure die casting can produce parts with intricate features, undercuts, and thin walls that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with other manufacturing methods.
High Production Rates: The process is highly automated, allowing for rapid production of large quantities of parts.
Cost-Effectiveness: For high-volume production, pressure die casting can be a cost-effective manufacturing solution.


Aluminium gravity die casting parts
Aluminum Gravity Die Casting Parts: A Versatile and Cost-Effective Solution Aluminum gravity die casting, also known as permanent mold casting, is a casting process where molten aluminum is poured into a reusable metal mold under the force of gravity. This method produces high-quality castings with good dimensional accuracy and surface finish. Key Advantages of Aluminum Gravity Die Cast Parts: Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to high-pressure die casting, gravity die casting generally has lower tooling costs, making it suitable for lower-volume production runs. Good Mechanical Properties: The slower cooling rate in gravity die casting results in castings with improved mechanical properties, such as higher ductility and impact strength. Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of part sizes and complexities, from small components to larger, more intricate shapes. Improved Surface Finish: Generally produces a smoother surface finish compared to sand casting. Reduced Porosity: The controlled cooling in the metal mold helps minimize porosity in the castings.Material Chemical Analysis
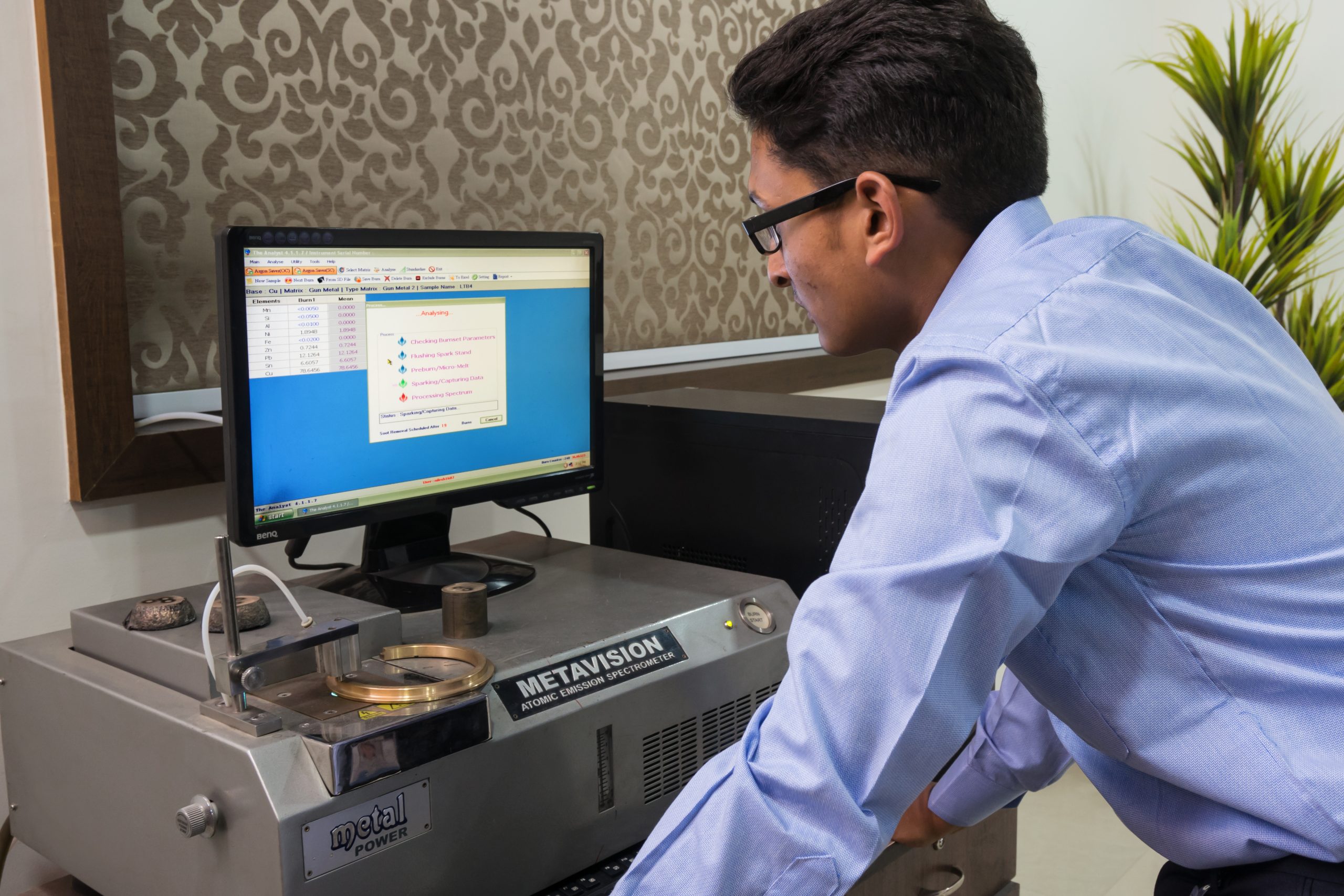
Material chemical analysis is a crucial process that involves determining the chemical composition of a material. It’s essential for various industries, including manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, environmental monitoring, and research.
Key Goals of Material Chemical Analysis:
• Verify Material Composition: Ensure that a material meets specific specifications or standards.
• Quality Control: Monitor the consistency and purity of materials during production.
• Failure Analysis: Investigate the cause of material failures by identifying impurities or unexpected elements.


Bronze Parts Machining
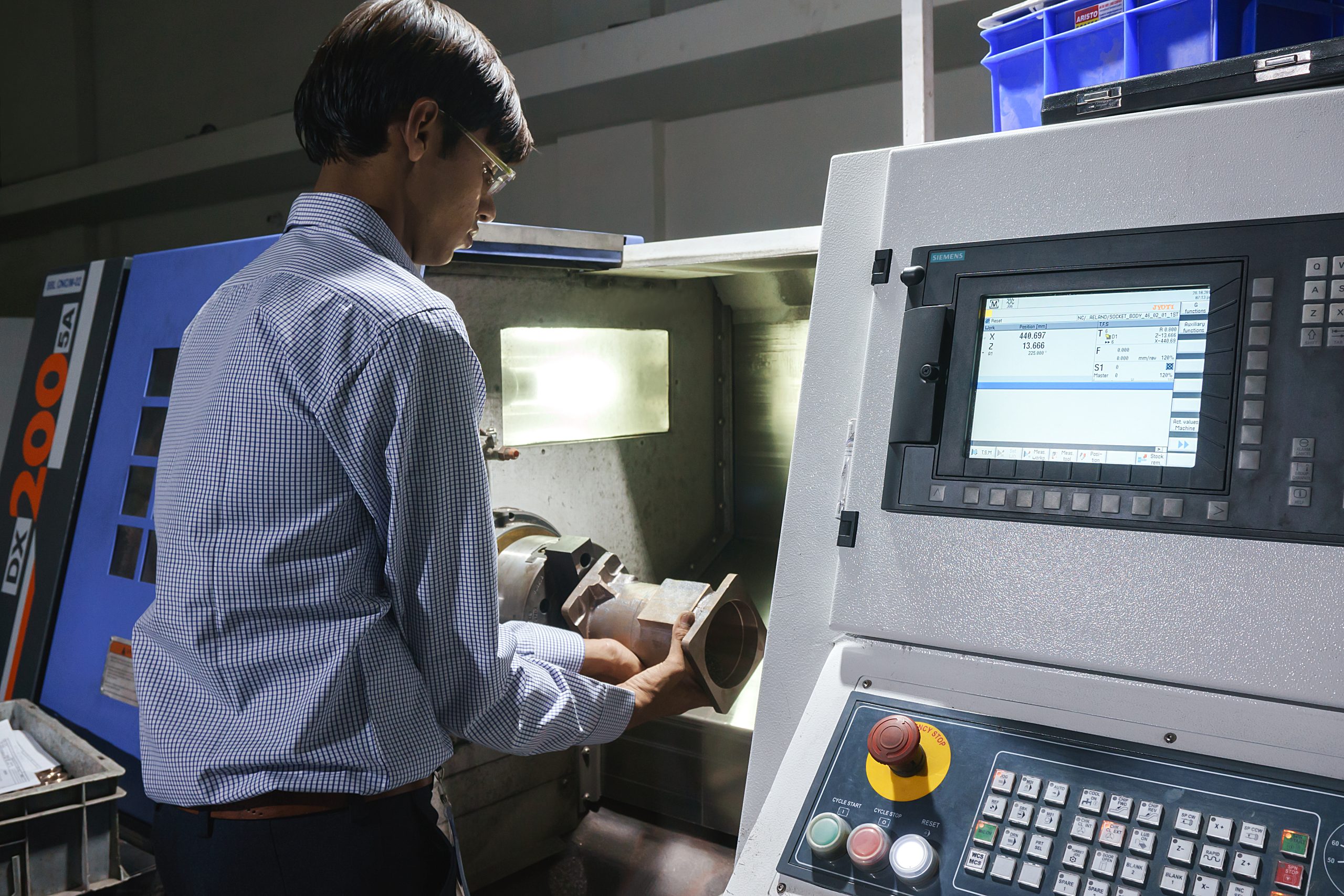
CNC Turning of Bronze Parts: A Precision Approach
CNC turning is a highly effective method for machining bronze components, leveraging the material’s excellent machinability and the precision of CNC technology.
Why CNC Turning for Bronze?
Complex Shapes: CNC machines can accurately create intricate shapes and profiles in bronze, including threads, tapers, and complex contours.
High Precision: Bronze’s machinability allows for tight tolerances and excellent surface finishes, crucial for many applications.
Efficiency: Automation significantly increases production speed and reduces labor costs compared to manual methods.
Consistency: CNC machines ensure consistent part quality and minimize variations.
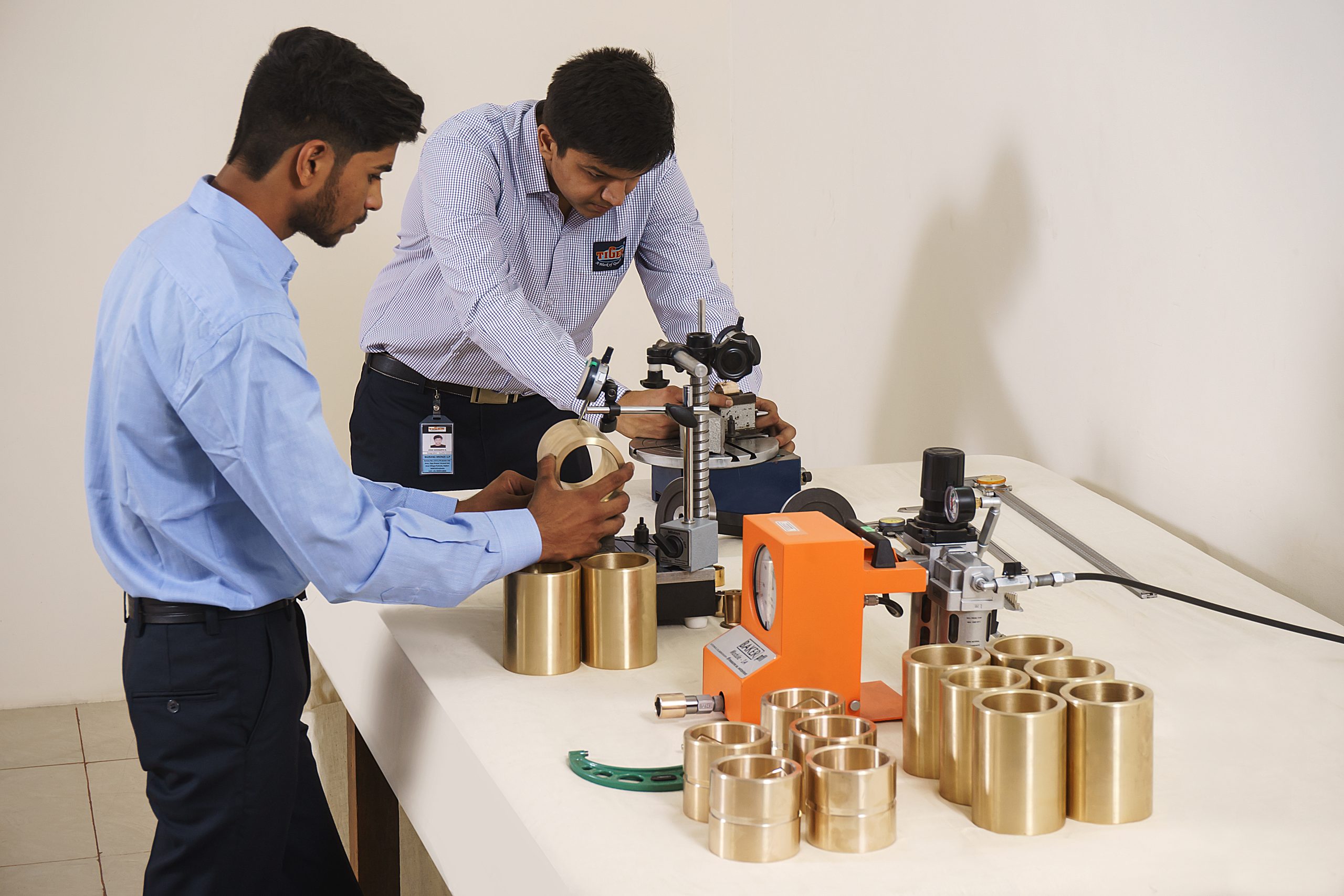
Diamension Inspection
Bronze Parts Inspection Methods:
• Visual Inspection: A preliminary check for obvious defects like cracks, porosity, or dimensional inconsistencies.
• Calipers and Micrometers: Handheld tools for measuring linear dimensions with high accuracy.
• Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs): Highly precise machines that can measure complex shapes and features with extreme accuracy.
• Optical Comparators: Used to compare the part’s profile to a master template or projected image.
Importance of Dimensional Inspection:
• Ensuring Functionality: Accurate dimensions are crucial for the proper functioning of bronze parts, especially in critical applications like marine hardware, industrial machinery, and automotive components.
• Meeting Specifications: Dimensional inspection ensures that the parts meet the specified tolerances and requirements defined in the design drawings.
• Quality Control: It helps identify and rectify any deviations from the desired dimensions, ensuring consistent quality and minimizing defects.
• Customer Satisfaction: Delivering parts that meet or exceed customer expectations is essential for maintaining customer satisfaction and building long-term relationships.
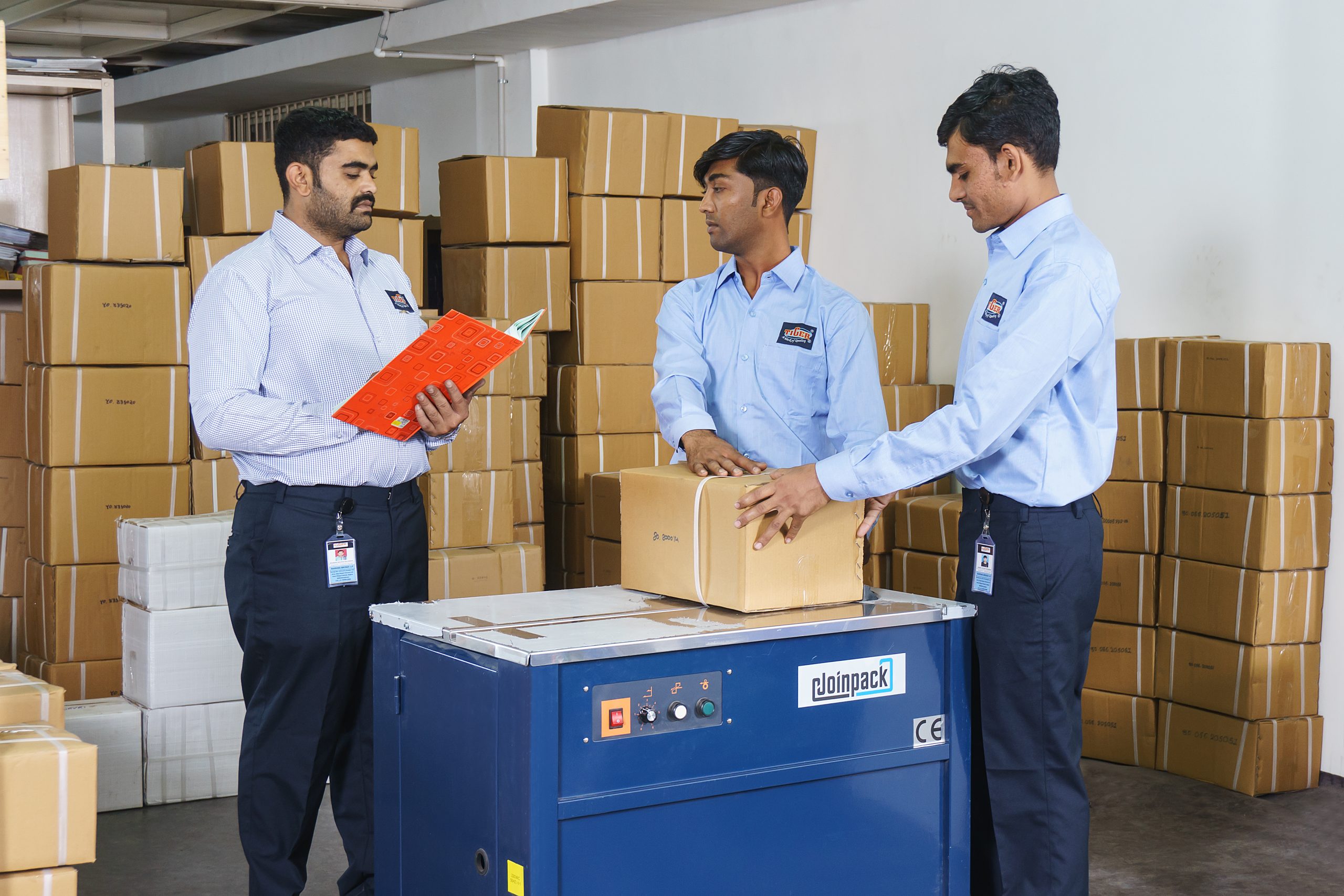


Bronze Parts Packaging
Protecting Your Investment Proper packaging of bronze parts is crucial to ensure they arrive at their destination in pristine condition, safeguarding their quality and preventing damage during transportation and handling. Here are some key considerations for packaging bronze parts:
1. Material Selection:
Corrugated Cardboard Boxes: A versatile and cost-effective option for most bronze parts. Choose boxes with sufficient thickness and internal bracing to withstand stacking and transportation stresses.
Wooden Crates: Ideal for larger, heavier, or more delicate bronze components. Wood provides excellent protection against shock and vibration.
Plastic Containers: Suitable for smaller parts or those requiring protection from moisture or chemicals.
2. Protective Packaging Materials:
Bubble Wrap: Provides cushioning and shock absorption for delicate parts.
Foam Inserts: Custom-cut foam inserts can provide precise fitting and secure holding for individual parts or sets.
Desiccant Packs: Help to absorb moisture and prevent corrosion, especially important for long-term storage or transportation in humid environments.
VCI (Vapor Corrosion Inhibitors): These special films or papers emit vapors that form a protective layer on the metal surface, preventing corrosion. Individual Part Wrapping: Wrap each part individually in protective materials like bubble wrap or VCI film before placing them in the main container. Labeling and Marking: Clearly label each package with relevant information, such as part number, quantity, and any special handling instructions.