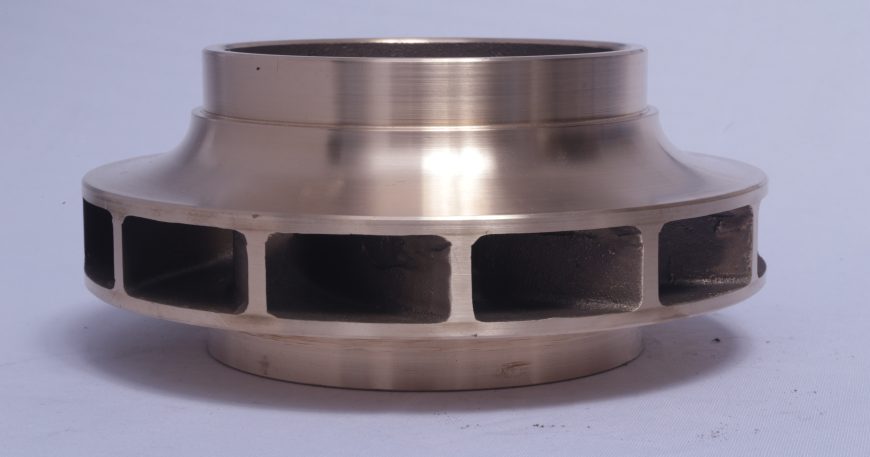
Bismuth bronze is a versatile alloy with a wide range of applications, primarily due to its lead-free composition, good machinability, and corrosion resistance. Here are some common ways bismuth bronze is used:
Plumbing and Waterworks:
- Faucets and fittings: Its lead-free nature makes it ideal for components in contact with drinking water, complying with regulations like the Reduction of Lead in Drinking Water Act.
- Valves and pumps: Bismuth bronze’s strength and corrosion resistance ensure reliable performance in water systems.
- Pipe fittings: Durable and safe for potable water, bismuth bronze fittings are used in residential and commercial plumbing.
- Water pump impellers: The alloy’s resistance to wear and corrosion makes it suitable for pump components.
Industrial Applications:
- Bearings and bushings: Bismuth bronze offers good wear resistance and lubricity, making it suitable for bearing applications.
- Gears and other machine parts: Its machinability and strength allow for the production of complex parts.
- Housings and structural components: Bismuth bronze can be used for structural elements requiring corrosion resistance.
Other Uses:
- Decorative items: The alloy’s attractive appearance and ability to hold a polish make it suitable for decorative applications.
- Musical instruments: Some musical instrument components may be made from bismuth bronze.
- Marine applications: Its corrosion resistance makes it suitable for use in marine environments.
Advantages of Bismuth Bronze:
- Lead-free: Environmentally friendly and safe for use in contact with drinking water.
- Good machinability: Easy to machine into complex shapes.
- Corrosion resistance: Suitable for use in harsh environments.
- Good wear resistance: Offers durability in moving parts.
- Attractive appearance: Can be polished to a high sheen.
Overall, bismuth bronze is a versatile material with a wide range of applications, particularly in plumbing and industrial sectors where its lead-free composition and performance characteristics are valued.
Key properties:
- Lead-free
- Good machinability (70% compared to free-cutting brass)
- Good polishing and plating characteristics
- Better castability at lower temperatures
- Superior microstructural characteristics
Applications:
- Faucets
- Housings
- Small gears
- Pipe fittings
- Plumbing goods
- Pump components
- Water pump impellers
Chemical composition:
- Copper (Cu): 85.0 – 89.0%
- Tin (Sn): 6.0 – 7.5%
- Lead (Pb): 0.09% max
- Zinc (Zn): 2.0 – 4.0%
- Iron (Fe): 0.20% max
- Nickel (Ni): 1.00% max
- Antimony (Sb): 0.35% max
- Phosphorus (P): 0.10% max
- Sulfur (S): 0.08% max
- Aluminum (Al): 0.005% max
- Bismuth (Bi): 1.7 – 2.7%
- Silicon (Si): 0.005% max
Mechanical properties:
- Tensile strength: 30 ksi (207 MPa) min
- Yield strength: 14 ksi (97 MPa) min
- Elongation in 2 in. or 50 mm: 6% min
Physical properties:
- Melting point – liquidus: 1855°F (1012°C)
- Melting point – solidus: 1445°F (785°C)
- Density: 0.321 lb/in3 at 68°F (8.89 gm/cm3 at 20°C)
- Specific gravity: 8.89
- Electrical conductivity: 14.5% IACS at 68°F (0.084 MegaSiemens/cm at 20°C)
- Thermal conductivity: 38.0 Btu·ft/(hr·ft2·°F) at 68°F (65.8 W/m·°K at 20°C)
- Coefficient of thermal expansion: 10 x 10-6 per °F (68-392°F) (17.3 x 10-6 per °C)
- Specific heat capacity: 0.093 Btu/lb/°F at 68°F (389.6 J/kg·°K at 293°K)
- Modulus of elasticity in tension: 16,900 ksi (116,522 MPa)
Fabrication properties:
- Soldering: Excellent
- Brazing: Good
- Oxyacetylene welding: Not recommended
- Gas shielded arc welding: Not recommended
- Coated metal arc welding: Not recommended
Equivalent specifications:
- CDA C89835
- UNS C89835
- B04 bronze
- Lead-free bronze
- Bismuth bronze
- Copper-bismuth bronze
- Lead-free bismuth bronze
- Bismuth tin bronze
- Lead-free bismuth tin bronze